Escape Walkthrough: Exploiting Whitelisting and Privilege Escalation
Walkthrough of Vulab's Machine Escape
Recon
I started with a standard Nmap scan to discover open TCP and UDP ports:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
sudo nmap -T4 -sS -n -Pn --disable-arp-ping --stats-every=5s -F 10.10.123.152
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-10-09 00:58 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.123.152
Host is up (0.14s latency).
Not shown: 99 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
sudo nmap -T5 -sU -n -Pn --disable-arp-ping --stats-every=5s -p- 10.10.123.152 --max-retries 0
- T4: Sets the timing template for faster scanning.
- sS: Performs a TCP SYN scan.
- n: Disables DNS resolution.
- Pn: Skips host discovery (pinging).
- F: Scans the top TCP ports.
- sU: Performs a UDP scan
The initial full scan and limited scan revealed only one open port: 3389, which is the default port for RDP connections.
Some Information about RDP Protocol
Developed by Microsoft, the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is designed to enable a graphical interface connection between computers over a network. To establish such a connection, RDP client software is utilized by the user, and concurrently, the remote computer is required to operate RDP server software. This setup allows for the seamless control and access of a distant computer’s desktop environment, essentially bringing its interface to the user’s local device.
Enumerating the OS and RDP Version
I used Nmap to enumerate the operating system and the RDP service version running on the machine:
1
sudo nmap -T4 -A -n -Pn --disable-arp-ping --stats-every=5s -p 3389 10.10.123.152
Explanation:
-T4: Sets the speed of the scan.-A: Enables OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute.-n: Skips DNS resolution for faster scanning.-Pn: Treats the host as online without pinging it.--disable-arp-ping: Avoids using ARP ping for host discovery, going directly for the port scan.-p 3389: Focuses the scan on the RDP port (3389).
Scan Results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
|_ssl-date: 2024-10-09T05:05:21+00:00; -1s from scanner time.
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: ESCAPE
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: ESCAPE
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: ESCAPE
| DNS_Domain_Name: Escape
| DNS_Computer_Name: Escape
| Product_Version: 10.0.19041
|_ System_Time: 2024-10-09T05:05:16+00:00
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Escape
| Not valid before: 2024-10-08T03:30:56
|_Not valid after: 2025-04-09T03:30:56
- The RDP service is running Microsoft Terminal Services on Windows version 10.0.19041.
- The
rdp-ntlm-infoscript reveals domain information and version details. - The warning indicates that the OS scan may be unreliable due to the absence of a closed TCP port, which affects the accuracy of the OS fingerprinting.
Scanning with Metasploit
Using Metasploit, I scanned the RDP service for more details:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
msf6 > search rdp_scanner
msf6 > use 0
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/rdp/rdp_scanner) > set RHOSTS 10.10.123.152
RHOSTS => 10.10.123.152
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/rdp/rdp_scanner) > set RPORT 3389
RPORT => 3389
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/rdp/rdp_scanner) > run
[*] 10.10.123.152:3389 - Detected RDP on 10.10.123.152:3389 (name:ESCAPE) (domain:ESCAPE) (domain_fqdn:Escape) (server_fqdn:Escape) (os_version:10.0.19041) (Requires NLA: No)
[*] 10.10.123.152:3389 - Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
NLA is disabled, which means that any user can attempt to connect without being prompted for authentication initially. This creates a potential risk for unauthorized access. With Network Level Authentication (NLA) disabled, any user can access the RDP login screen, posing a severe security risk. For accounts like KioskUser0 that allow password-free login, immediate access is granted, bypassing any security checks. This setup invites not only unauthorized access but also potential brute-force attacks on other user accounts
With NLA disabled on the target machine, I attempted to establish a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connection using xfreerdp with random username. 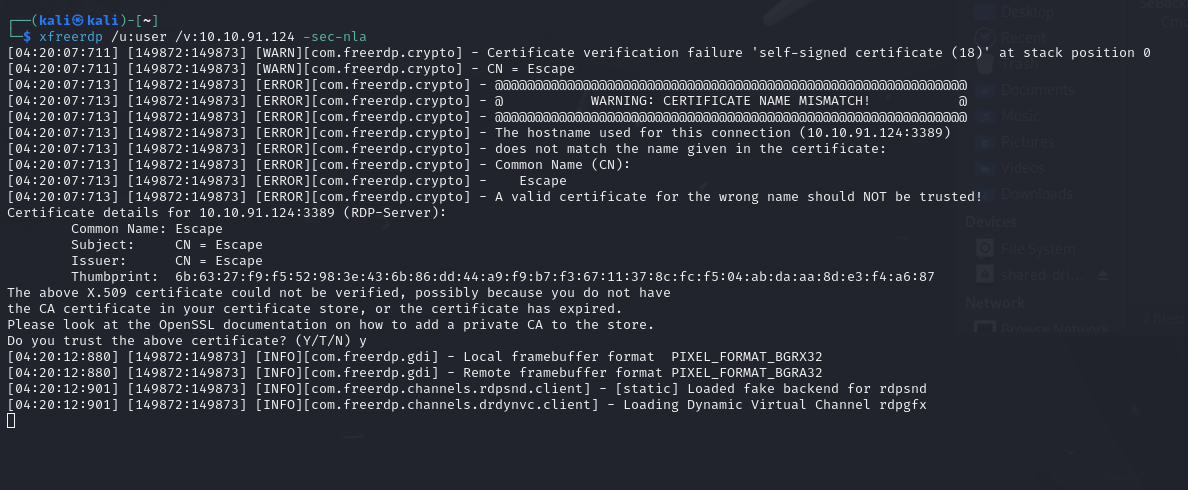
Upon successfully connecting to the machine via RDP, I was greeted by a distinctive blue login screen explicitly advising to log in as KioskUser0 without requiring a password. 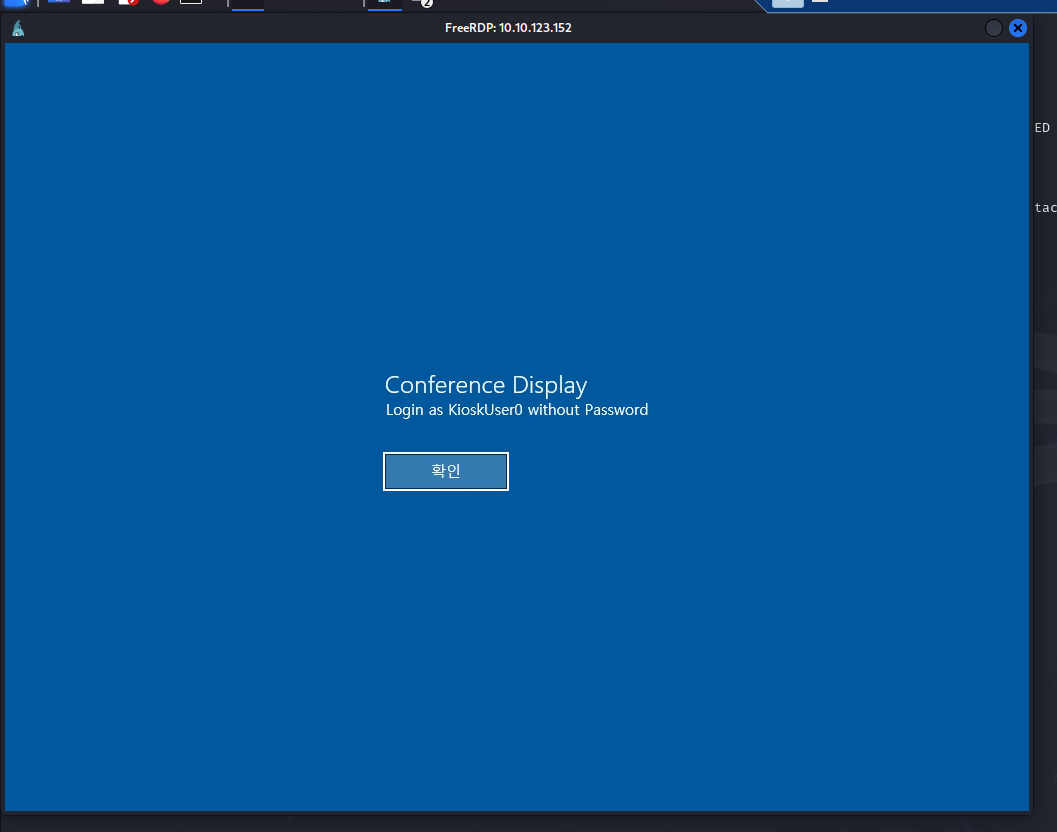
Upon successful login, Changed the language settings from korean to English to clearly understand the error messages or system prompts.
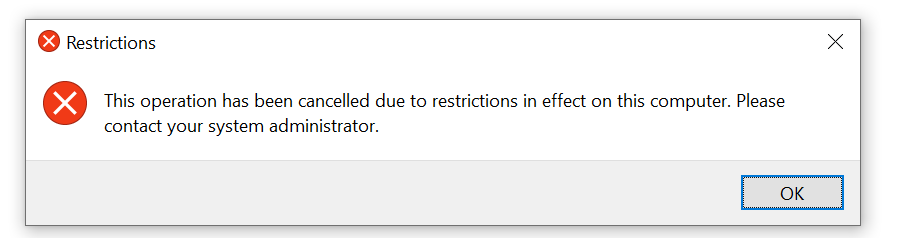
The “kioskuser0” has limited access to file System and applications. The only accessible area in the file system was the Downloads folder and the Microsoft Edge was the only application the user can execute.
If the user attempt to access any unauthorized folder, an error message was seen as show below
Exploring through Windows Explorer revealed that the interim flag was located on “KioskUser0”’s Desktop.
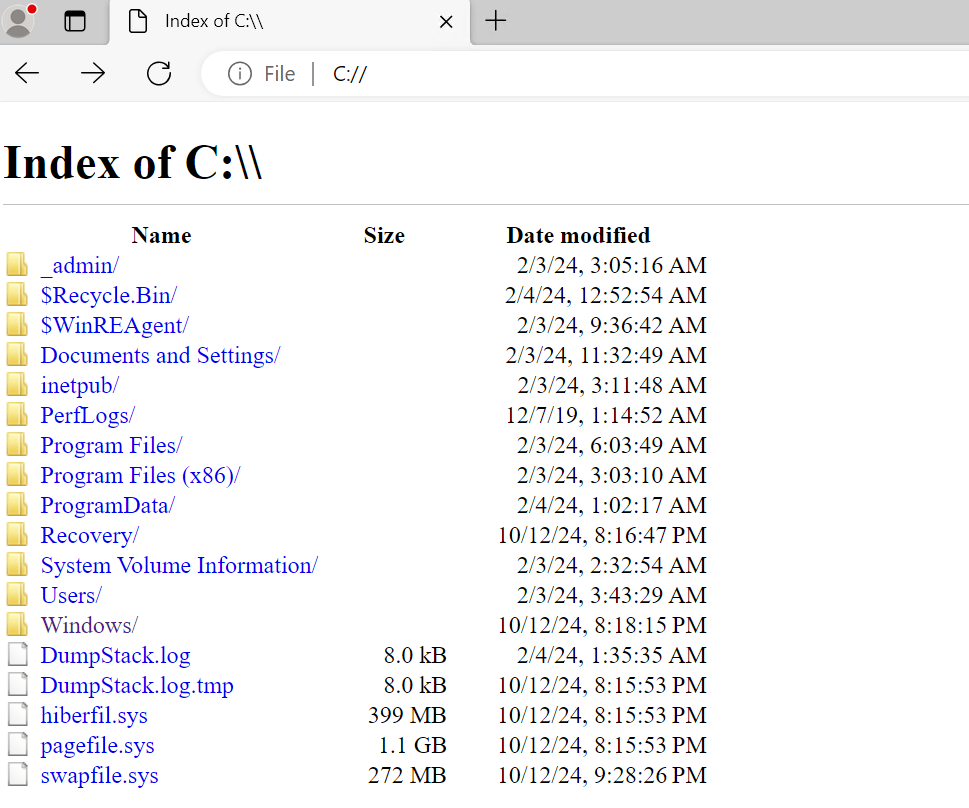
The file system could also be accessed via Microsoft Edge using the file:///C:/ protocol, revealing the same directory structure. The file:///C:/ protocol is a way to access the file system of a computer directly through a web browser.
Navigated to the user’s Desktop folder and successfully retrieved the flag.
Privilege escalation to Administrator
Harvesting Credentials - 1
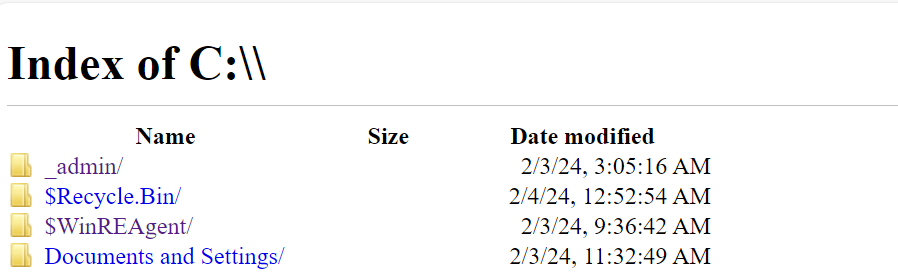
While browsing the file system of the machine, I came across an interesting folder named _admin located at C:\
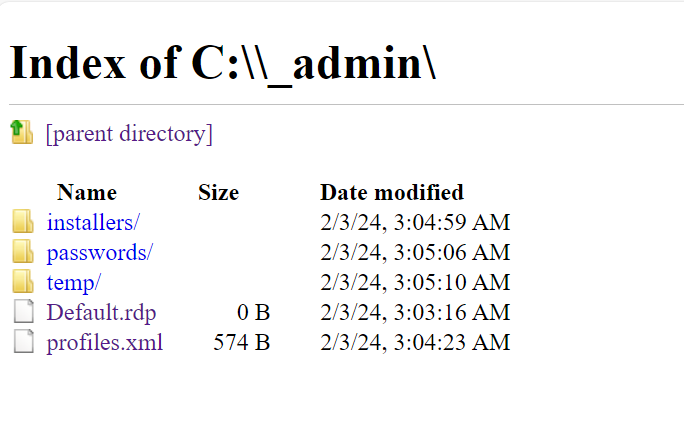
Inside the _admin folder, most of the files were either empty or not particularly noteworthy, except for profiles.xml.
The profiles.xml file contained interesting information about an admin profile:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<!-- Remote Desktop Plus -->
<Data>
<Profile>
<ProfileName>admin</ProfileName>
<UserName>127.0.0.1</UserName>
<Password>JWqkl6IDfQxXXmiHIKIP8ca0G9XxnWQZgvtPgON2vWc=</Password>
<Secure>False</Secure>
</Profile>
</Data>
I attempted to decode the password since it appeared to be a Base64 encoded string, but unfortunately, the decoding attempt was unsuccessful.
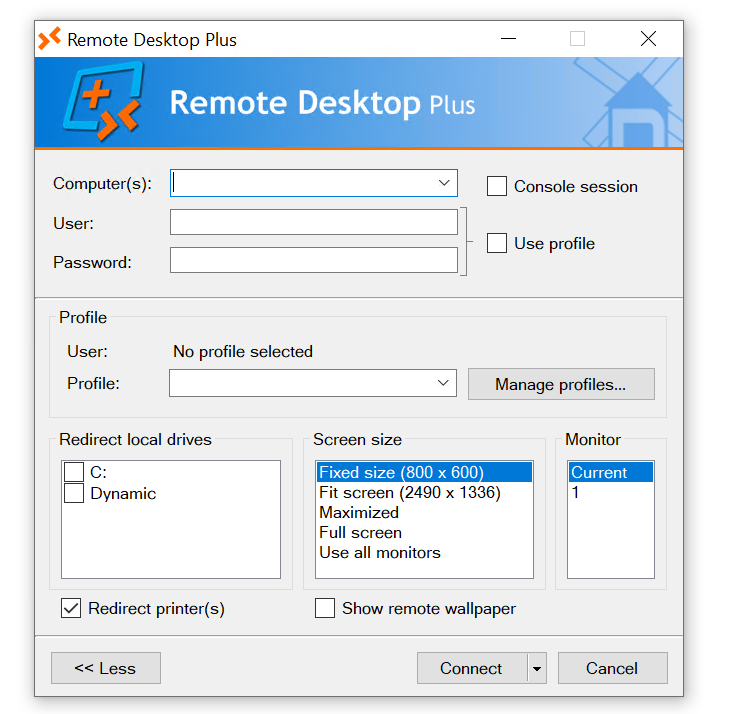
Later downloaded both Remote Desktop Plus and the profiles.xml file locally using msedge.exe for further analysis.
Since msedge.exe was whitelisted, I performed a trial and error to determine whether the exclusion was based on the name or path.
After renaming the downloaded Remote Desktop Plus application to msedge.exe, I was able to successfully execute it, as shown below:
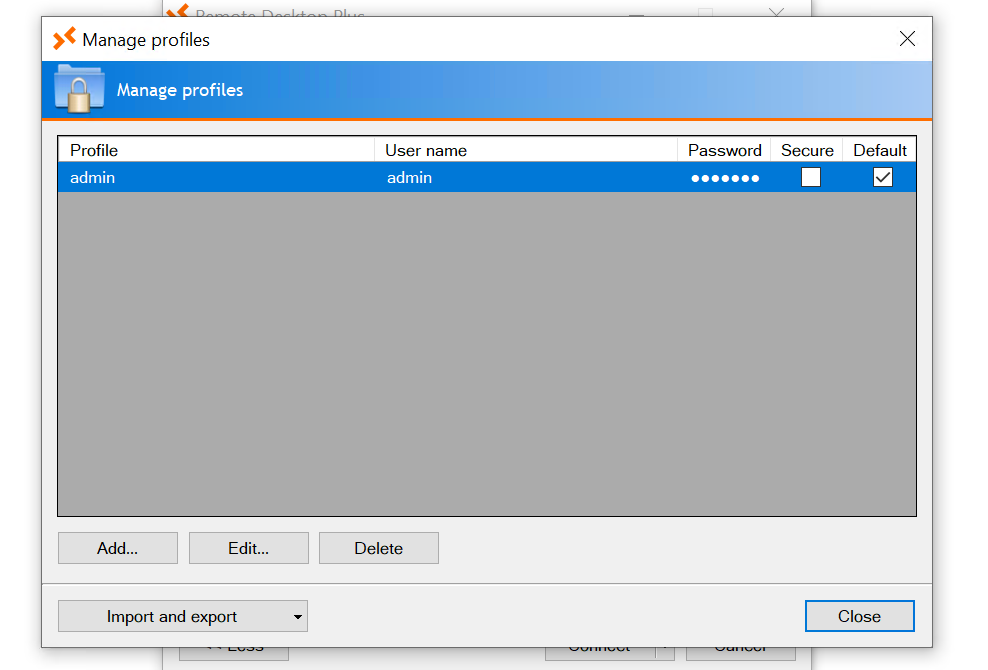
Later I imported the profile.xml to the remote desktop plus application.
The password length observed in the application’s profile manager differed from the one stored in profiles.xml, leading me to believe that the password was decrypted or decoded by the application in memory.
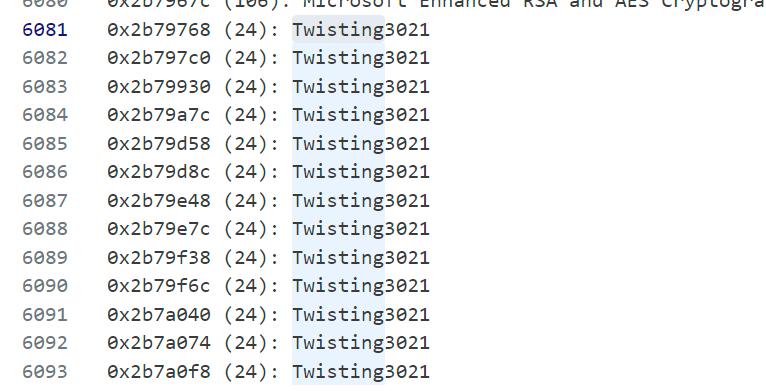
Since Copy & Paste was enabled on the machine, I transferred Process Hacker, renamed it to msedge.exe, and executed it.
Dumped the strings from the application’s process memory using Process Hacker, searching for anything interesting. After brute-forcing a few potential candidates, I successfully identified the password.
Escalating the privileges
Since any application with the name msedge.exe can be executed on the machine, I downloaded and renamed cmd.exe to msedge.exe, allowing me to run arbitrary commands.
Using this method, I logged in as the admin user via the runas command:
1
2
C:\Users\kioskUser0\Downloads>runas /user:ESCAPE\admin powershell
Enter the password for ESCAPE\admin:
Despite elevating to the admin user, I was still unable to access the Administrator’s directory at %USERS%.
Upon further research, I realized that the obtained shell had medium integrity, limiting my privileges. 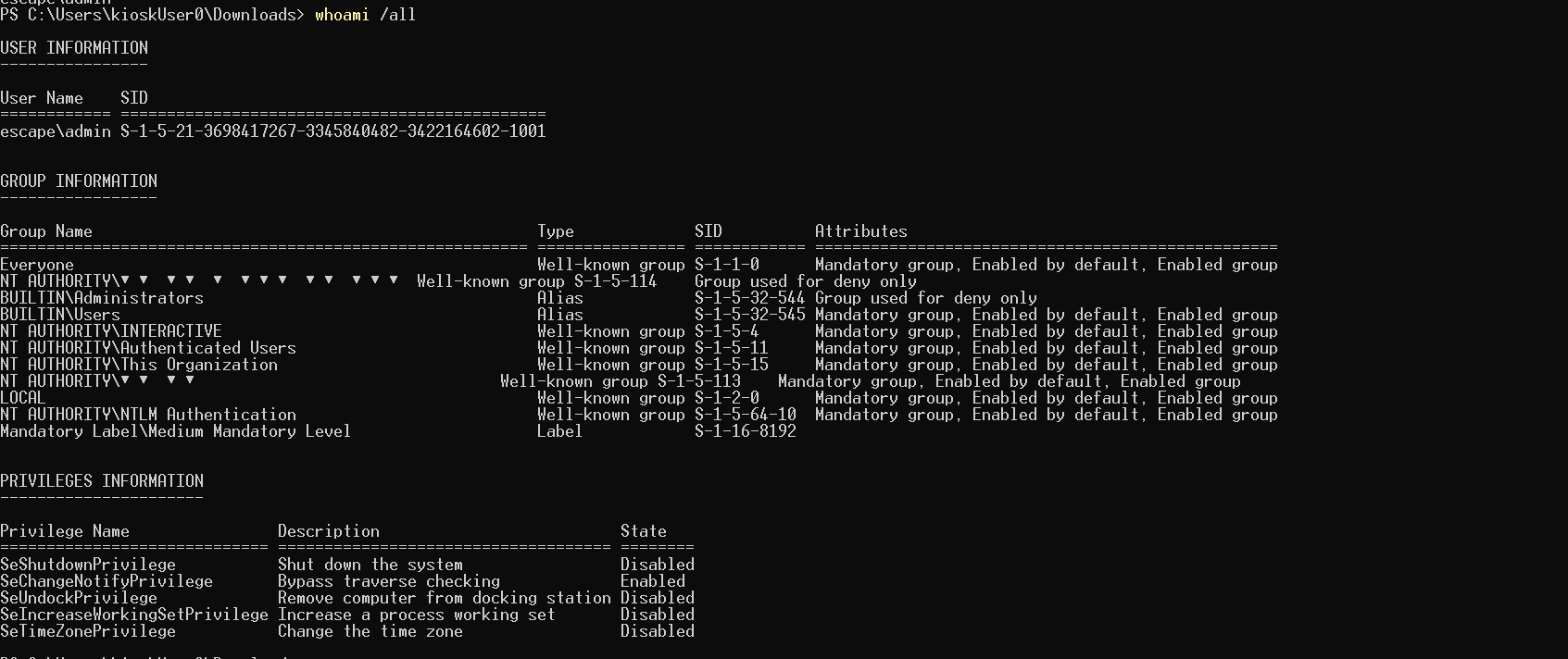
Medium: The default level for most activities, assigned to standard users and objects without specific integrity levels. Even members of the Administrators group operate at this level by default.
High: Reserved for administrators, allowing them to modify objects at lower integrity levels, including those at the high level itself.
UAC-Bypass Using netplwiz.exe Help Topics (GUI)
Obtained a SYSTEM Shell with the UAC Bypass
Disclaimer:
The techniques and tools discussed in this walkthrough are intended solely for educational purposes and to help improve cybersecurity awareness. Please conduct any penetration testing activities only on systems that you own or have explicit permission to test. Unauthorized access to computer systems is illegal and punishable by law. The author does not take responsibility for any misuse of the information provided